IGH/CCND1 ; IGH/MAF ; IGH/MAFB ; IGH/FGFR3 gene fusion detection probe (MAFB/IGH)
IGH/MAF Gene Fusion Probe Detection Kit - 100µL/10 Tests
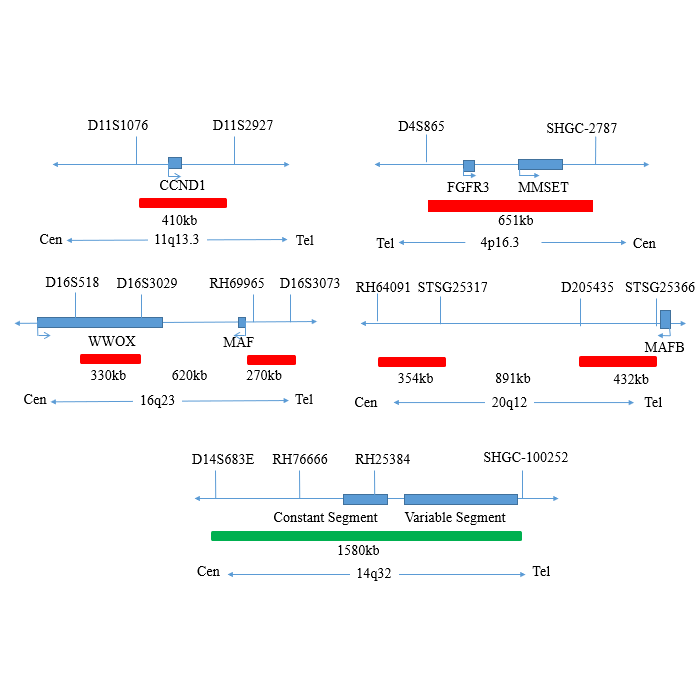
MAF (MAF BZIP Transcription Factor) protein encoded by this gene is a DNA-binding, leucine zipper-containing transcription factor that acts as a homodimer or as a heterodimer. Depending on the binding site and binding partner, the encoded protein can be a transcriptional activator or repressor. This protein plays a role in the regulation of several cellular processes, including embryonic lens fiber cell development, increased T-cell susceptibility to apoptosis, and chondrocyte terminal differentiation. Defects in this gene are a cause of juvenile-onset pulverulent cataract as well as congenital cerulean cataract 4 (CCA4). Two transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2010].
Immunoglobulins recognize foreign antigens and initiate immune responses such as phagocytosis and the complement system. Each immunoglobulin molecule consists of two identical heavy chains and two identical light chains. This region represents the germline organization of the heavy chain locus. The locus includes V (variable), D (diversity), J (joining), and C (constant) segments. During B cell development, a recombination event at the DNA level joins a single D segment with a J segment; this partially rearranged D-J gene is then joined to a V segment.
The rearranged V-D-J is then transcribed with the IGHM constant region; this transcript encodes a mu heavy chain. Later in development B cells generate V-D-J-Cmu-Cdelta pre-messenger RNA, which is alternatively spliced to encode either a mu or a delta heavy chain. Mature B cells in the lymph nodes undergo switch recombination, so that the V-D-J gene is brought in proximity to one of the IGHG, IGHA, or IGHE genes and each cell expresses either the gamma, alpha, or epsilon heavy chain. Recombination of many different V segments with several J segments provides a wide range of antigen recognition.
Additional diversity is attained by junctional diversity, resulting from the random addition of nucleotides by terminal deoxynucleotidyltransferase, and by somatic hypermutation, which occurs during B cell maturation in the spleen and lymph nodes. Due to polymorphism, the numbers of functional V, J, and D genes differ among individuals and some V, D, J, and C segments may be pseudogenes. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2017].
Product Main Components
This kit consists of MAF/IGH dual color probe
|
Component name |
Specifications |
Quantity |
Main components |
|
MAF/IGH dual color probe |
100μL/Tube |
1 |
MAF orange probe ; IGH green probe |
Intended use
The reagent carries out in situ hybridization staining on the basis of routine staining to provide doctors with auxiliary information for diagnosis. The test results are only for clinical reference and should not be used as the only basis for clinical diagnosis. Clinicians should comprehensively judge the test results in combination with the patient's condition, drug indications, treatment response and other laboratory test indicators.
Detection principle
Fluorescence in situ hybridization is a technique for directly observing specific nucleic acids in cells in vitro. According to the principle of base complementary pairing, the specific probe is complementary to the target sequence in the cell. Due to the fluorescence of the probe, the gene state of the hybrid probe and the target sequence can be clearly observed under the fluorescence microscope under the appropriate excitation light.
Applicable Instruments
Fluorescence microscopy imaging systems, including fluorescence microscopy and filter sets suitable for DAPI (367/452), Green (495/517), and Orange (547/565).